 --
STOCK
--
STOCK
|

| Products | State stock | Partner stock | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quantities (T) | Values(CFA) | Stock value (dollar $) | Capacity (T) | Quantities (T) | Values(CFA) | Stock value (dollar $) | Capacity (T) | |
| Maize | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Rice (Paddy) | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Sorghum | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Gari | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Bambara beans | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
Background
Stock monitoring activities are part of the Food Security Storage Support Project in West Africa.
Stock typology
Stocks in the ECOAGRIS framework are grouped into three large blocks:
- Institutional or public stocks
- Commercial or private stocks
- Proximity stocks
Institutional or public stocks
Public stocks are instruments for preventing and managing food crises. In most countries, particularly in the Sahel, the management of these stocks is entrusted to companies or national food security stock management offices. The following can be considered as institutional stocks: national security stocks or reserves; public food aid, intervention stocks or sovereignty stocks; the commercial regulatory stock, etc. All the security stock management offices in the region are grouped together in a network called "RESOGEST".
Commercial or private stocks
These are stocks held by private actors, associations and cooperatives of wholesale traders and large producers. These stocks are exclusively for commercial purposes. They are for the most part located in the major consumption and production inside or outside the main ones.
In total, a minimum of 215 consolidation and consumption markets will be evaluated at the end of the process in the 17 countries as part of the monitoring of Commercial stocks by the National Market Information System (MIF).
Minimum number of market required
| Pays | Minimum number of market required | Main Areas of Interest |
|---|---|---|
| Benin | 10 | Center to the north |
| Burkina | 15 | All |
| Cap Vert | 5 | All |
| Côte d’Ivoire | 10 | Center to the north |
| Gambie | 5 | All |
| Ghana | 10 | North |
| Guinée | 10 | Regional capitals |
| Guinée Bissau | 10 | Regional capitals |
| Liberia | 10 | Regional capitals |
| Mali | 20 | ALl |
| Mauritanie | 15 | All |
| Niger | 20 | ALl |
| Nigeria | 20 | North (13 states) |
| Sénégal | 15 | ALl |
| Sierre Leone | 10 | Regional capitals |
| Tchad | 20 | Regional capitals |
| Togo | 10 | Regional capitals |
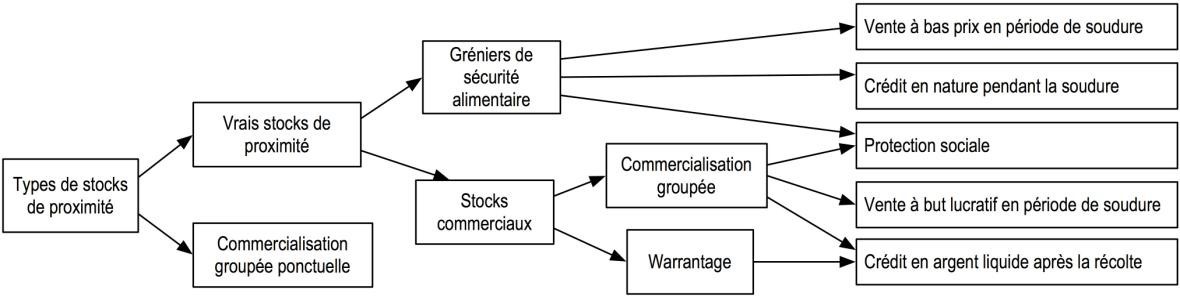
Proximity Stocks
Proximity stocks are formal or informal collective initiatives managed by small producers or associations to improve availability and access to food or increase incomes by buying grains from producers when prices are low and selling it when prices are profitable. These proximity stocks can be located in both deficit and surplus areas. These Proximty stocks constitute a first line of defence in the ECOWAS regional stockpiling strategy. The proximity stocks that are all cereal banks can be grouped together ; local food security warehouses ;commercial stocks for whole sales ; warrantages, etc.
Figure : Types of proximity stocks